Business Overview
Video Summary
What is
Biomass Energy?
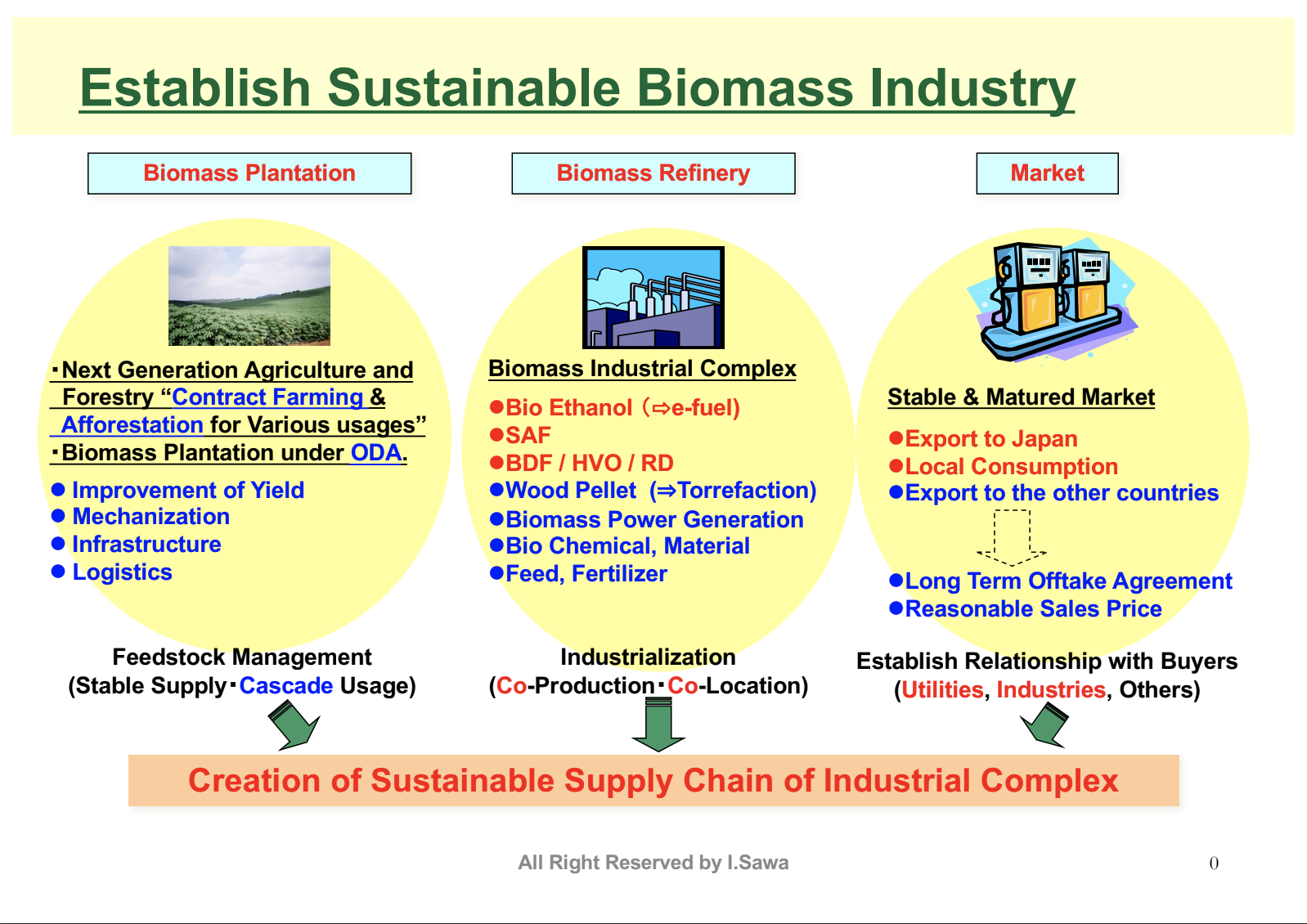
Biomass energy is a renewable energy source that serves as an alternative to fossil fuels. Specific examples include bioethanol as a substitute for gasoline, biodiesel as a replacement for diesel, and biomass pellets as an alternative to coal.
Biomass energy is an effective solution for climate change mitigation and energy security enhancement.
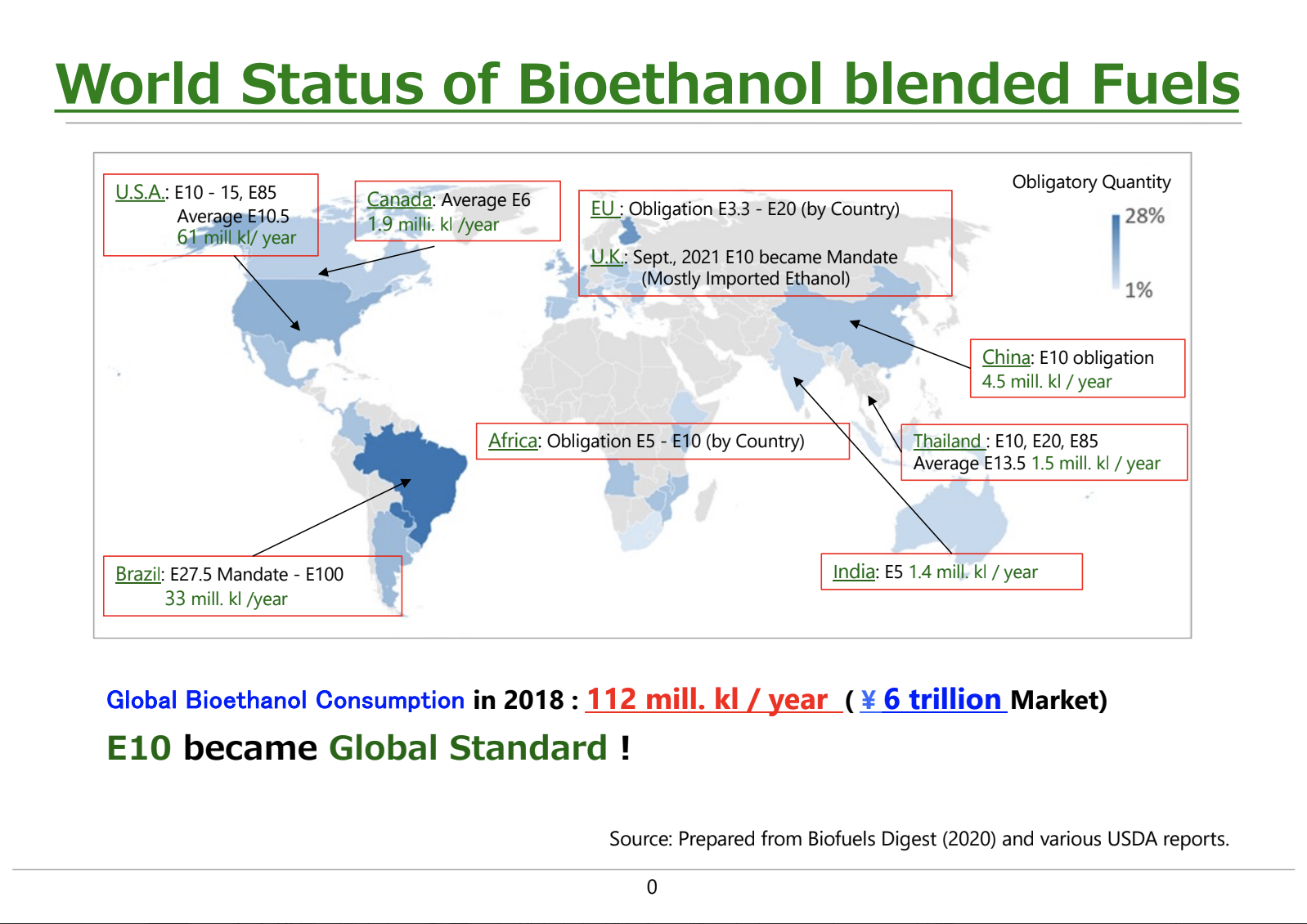
Current Status
of Bioethanol
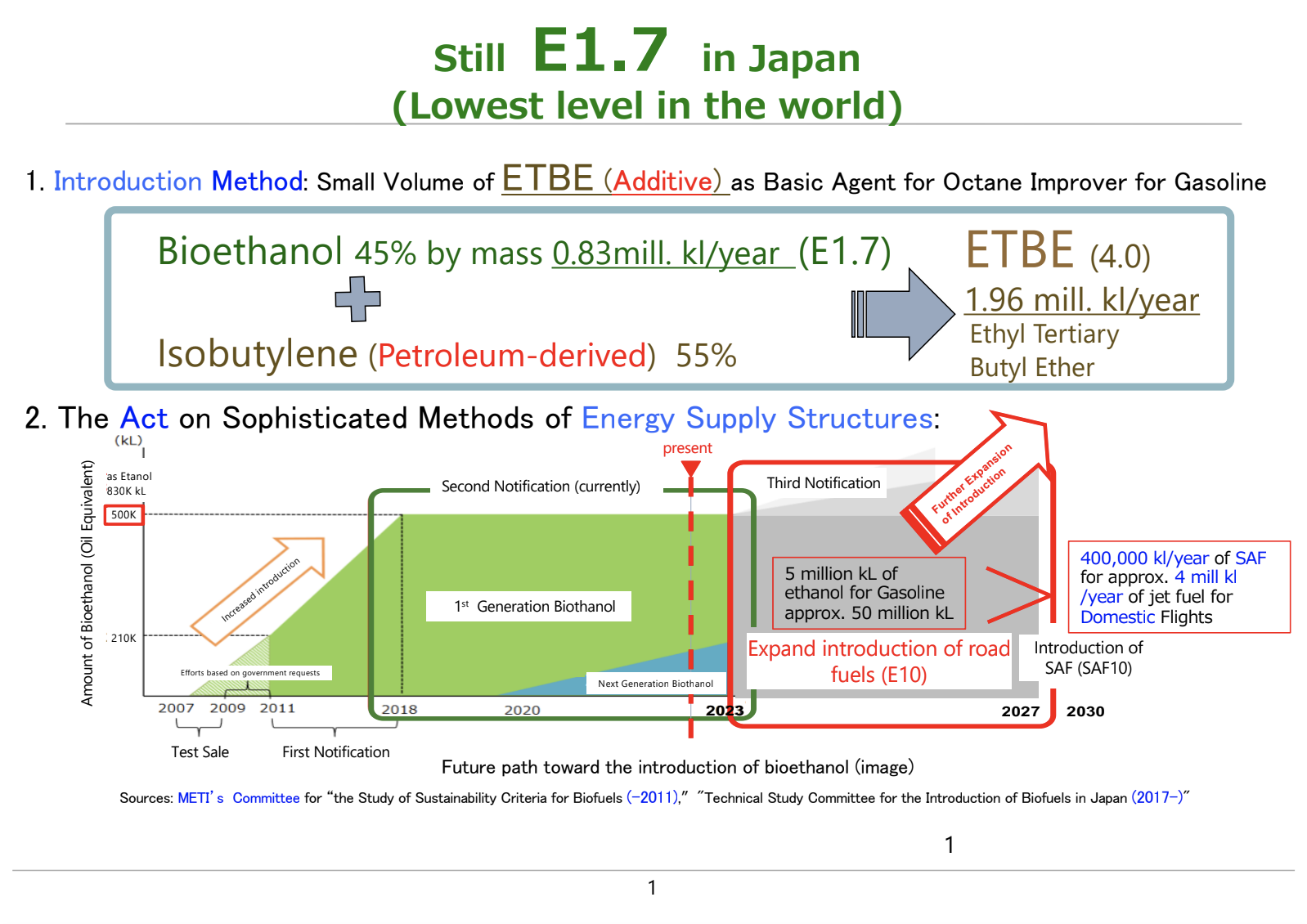
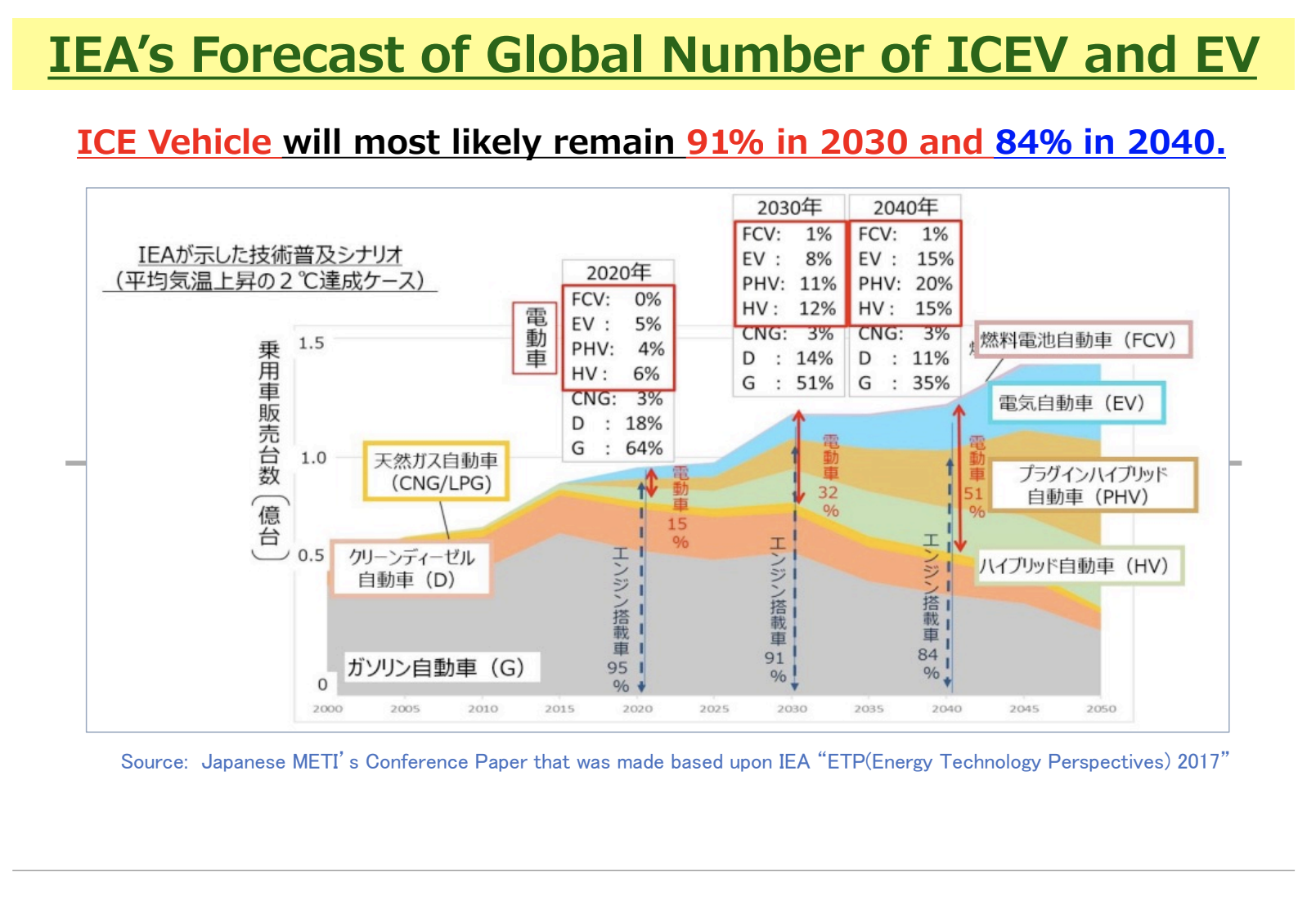
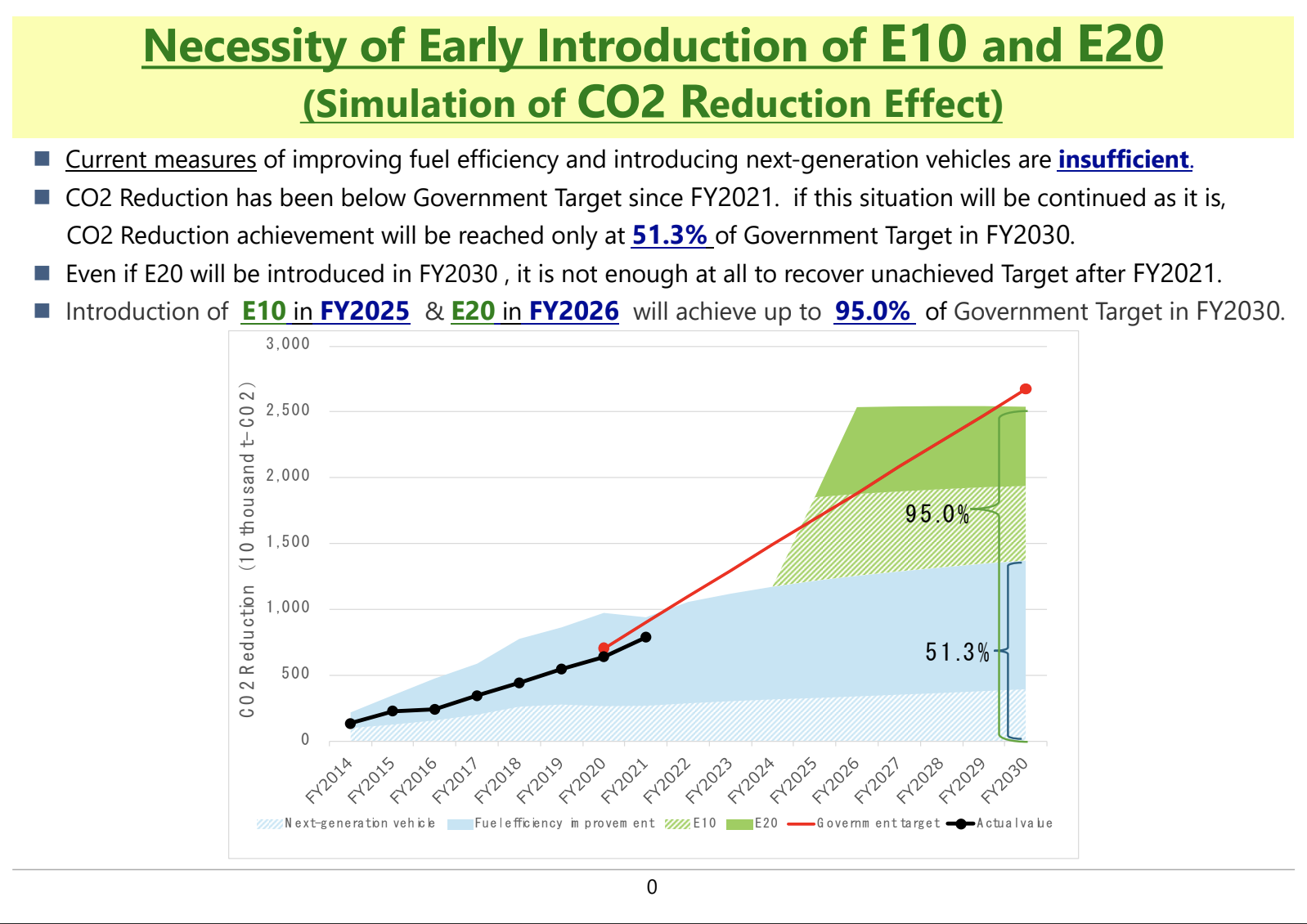
Globally, it is common for gasoline to contain more than 10% ethanol. However, in Japan, the ethanol blending ratio remains at a very low level of 1.7%.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) aims to increase the ethanol blending ratio to 10% (E10) by 2030 and 20% (E20) by 2040.


Environmental Impact
of Bioethanol
The use of bioethanol helps reduce CO₂ emissions by decreasing the consumption of fossil fuels.
CO₂ emissions from biofuel combustion are considered carbon-neutral, as the plants used to produce bioethanol absorb CO₂ through photosynthesis during their growth.
Bioethanol
and Food Competition
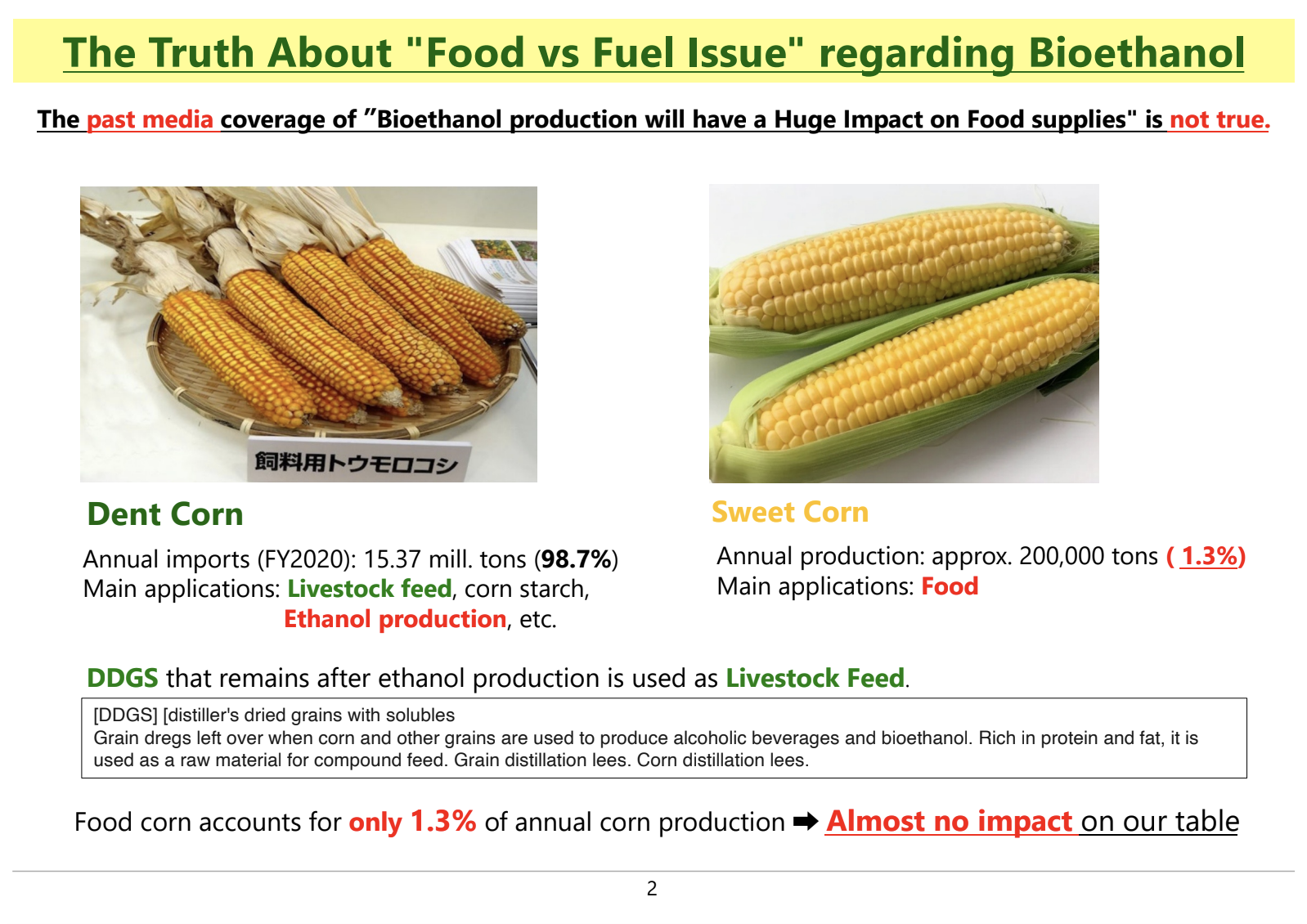
In the past, there were reports suggesting that bioethanol production competes with food supply. However, in reality, dent corn, which is primarily used for livestock feed, is the main raw material for bioethanol production.
Since sweet corn, which is used for human consumption, accounts for only about 1% of total corn production, its impact on the food supply is minimal.
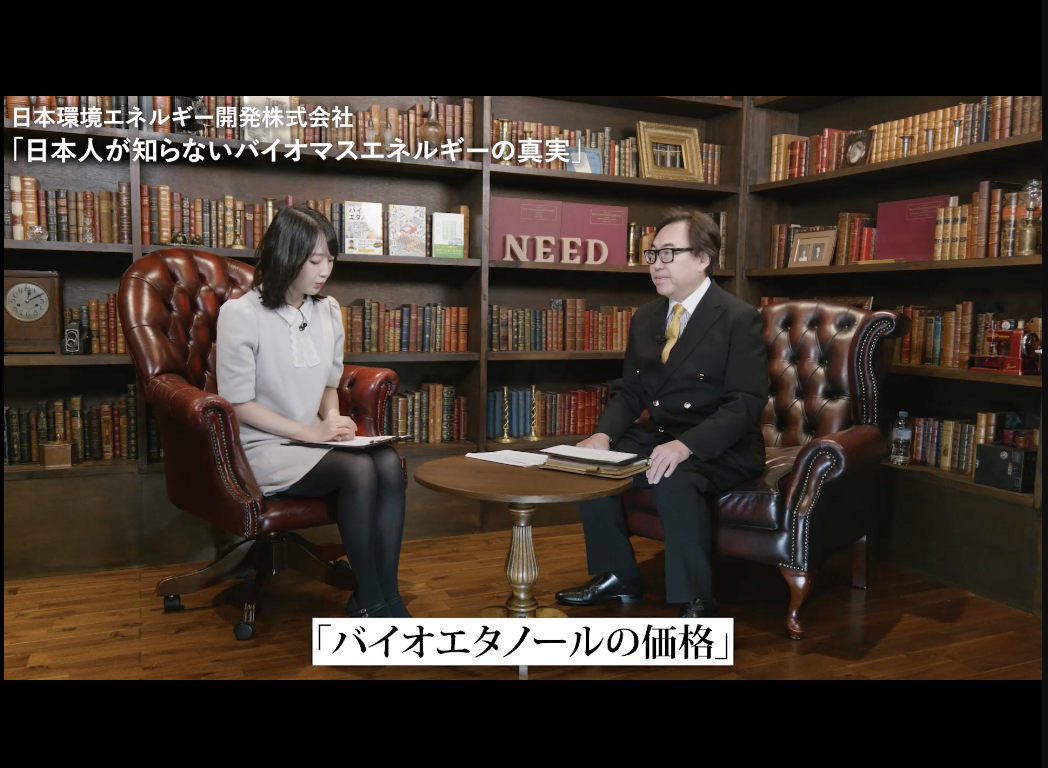
The Price of
Bioethanol
Previously, bioethanol was considered expensive. However, due to the surge in crude oil prices and the decline in corn prices, it has now become a more affordable energy source than gasoline.

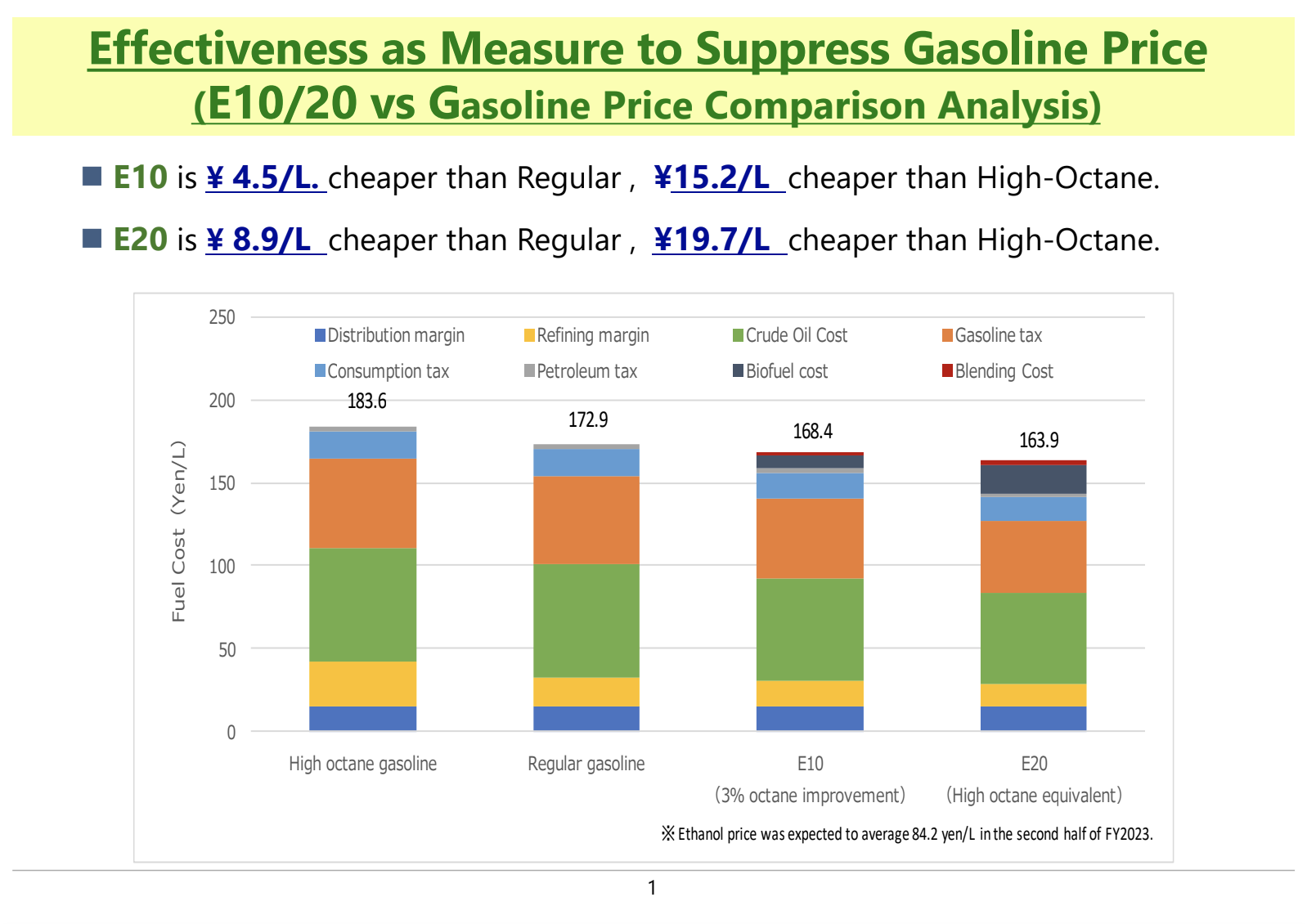
The Future of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
and Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to take a considerable amount of time, given that the average vehicle replacement cycle exceeds 20 years.
Additionally, there are supply challenges for rare metals required for batteries. As a measure to reduce CO₂ emissions from internal combustion engine vehicles, bioethanol is gaining attention as a promising alternative fuel.

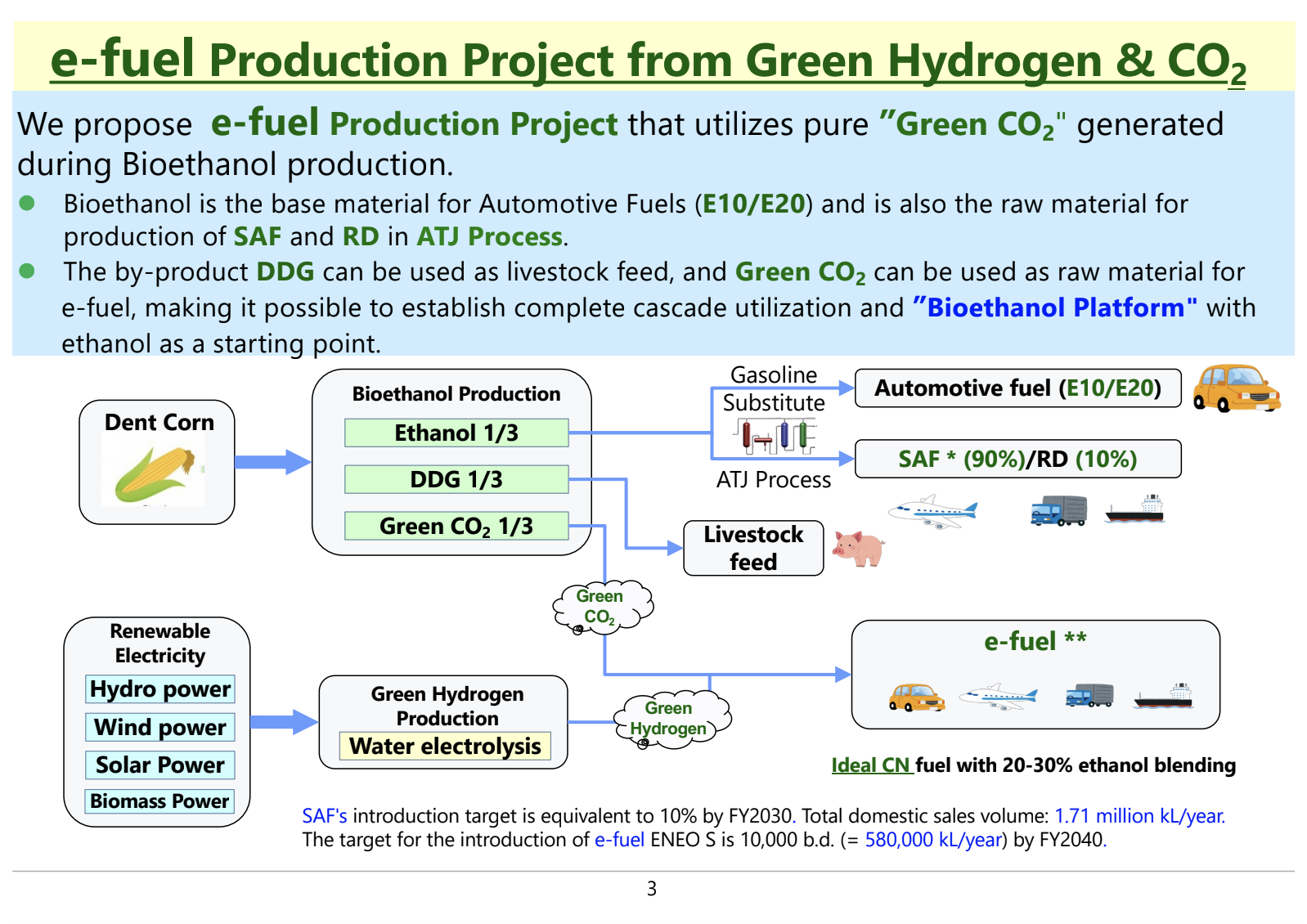
Synthetic Fuel (e-Fuel)
In the future, synthetic fuel (e-fuel) is expected to play a key role, and its production requires both hydrogen and CO₂.
There are considerations to utilize carbon-neutral, high-purity CO₂ emitted during ethanol production for the manufacturing of e-fuel.
Since e-fuel has a low octane rating, blending it with ethanol is an effective way to enhance its octane value.
Looking ahead, it is anticipated that 100% carbon-neutral fuel (e-fuel + ethanol) will serve as a complete substitute for gasoline.


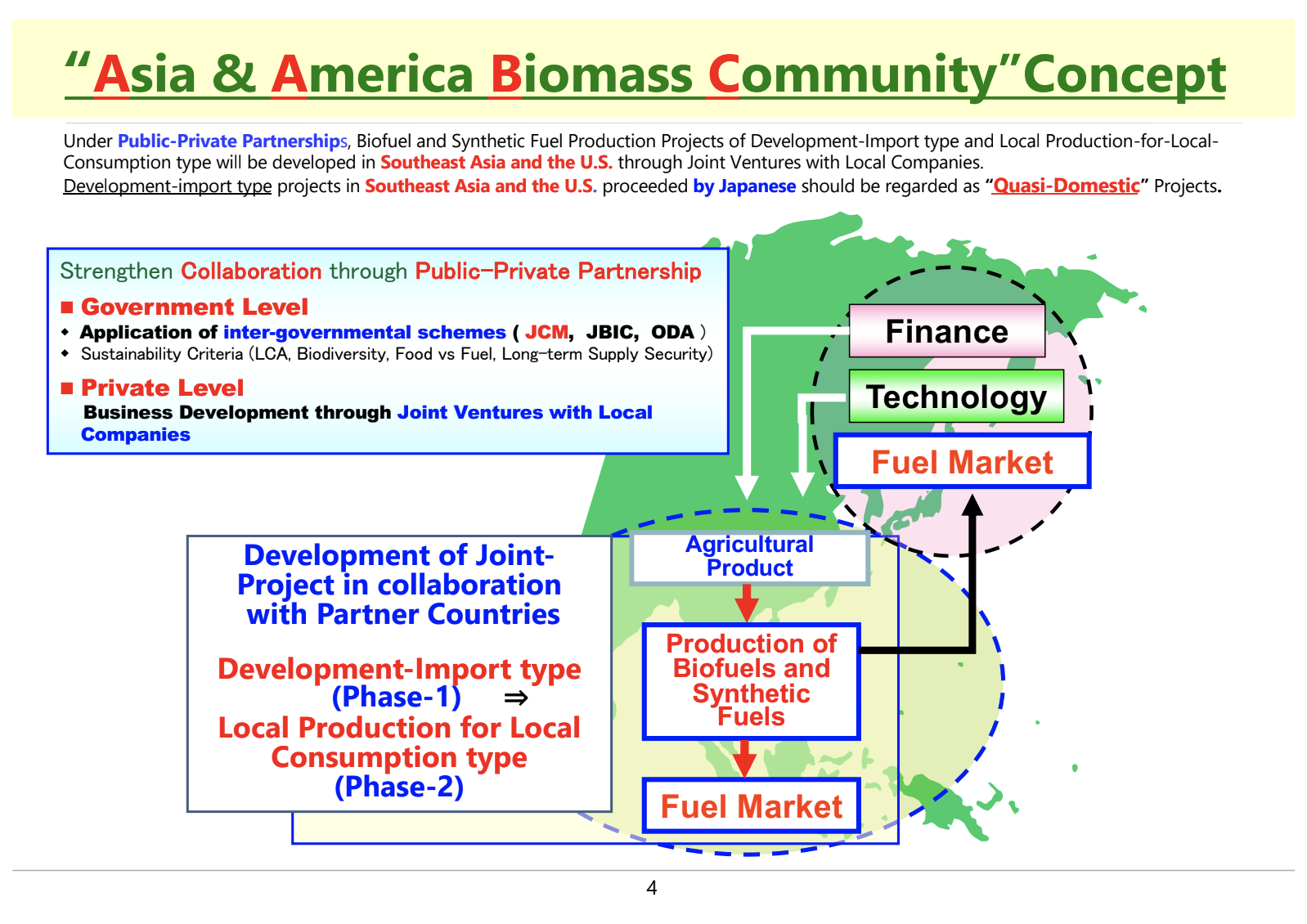
Asia & America Biomass Community Initiative